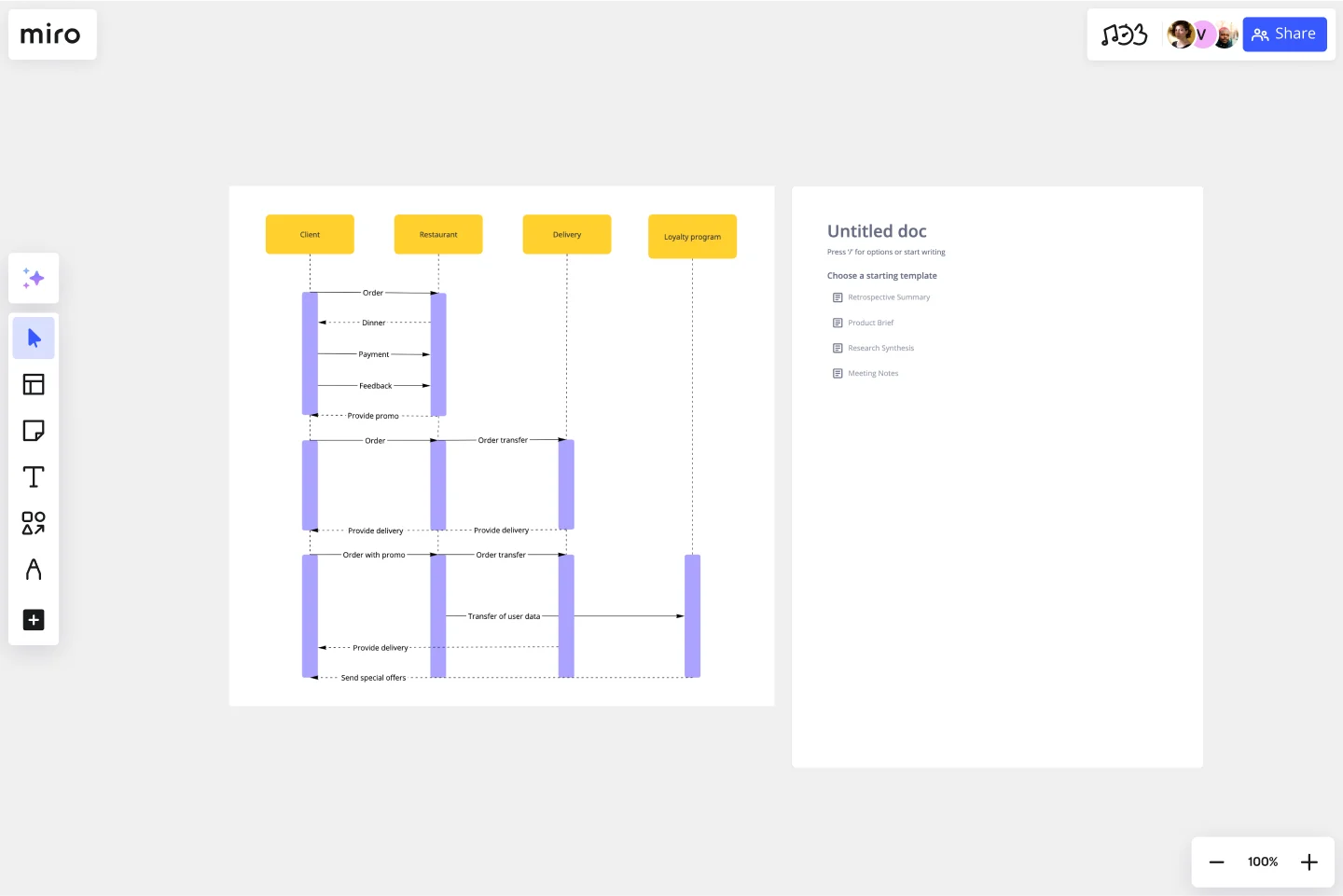
UML Sequence Diagram Template
Understand the order in which the events within a sequence interact with each other using Miro's UML sequence diagram template.
Available on Enterprise, Business, Education plans.
About the UML Sequence Diagram Template
A sequence diagram template is a tool that helps teams get a better overview of their work process, depicting object interaction in a system in sequential order. Many use a system sequence diagram to map the customer journey through an eCommerce store or to get a high-level overview of specific business functions. In the first scenario, the customer is the "actor" or external entity interacting with the diagram elements. The diagram for the second example does not necessarily need to have an "actor."
Teams also use the sequence diagram to analyze existing work systems. However, one of its primary use cases is in requirements documents for future systems implementation, so when staff or analysts design a new system, one or more sequence diagrams are used to showcase how this system will behave.
How to use the UML sequence diagram template
Miro is the perfect online sequence diagram tool to create your diagram from scratch and share it with your team. Miro also has its own template that you can customize to suit your needs. Simply select the UML sequence diagram template and then follow these steps:
1. Identify your lifelines
Lifelines represent the roles or object instances that are interacting. There can be two or more lifelines in a sequence. Each lifeline is placed in a box at the top of the diagram with a vertical dashed line below it.
2. Create messages
A message is an interaction between the lifelines. It is represented using a horizontal arrow. Seven different types of messages can be used in a sequence diagram.
3. Define your actor
An actor is an external entity that interacts with the sequence but is not a part of that sequence. In online shopping, for example, the "actor" is the customer, while the shopping system (e.g. "Add to cart"-"Total"-"Confirm order") is the sequence.
4. Add action bars
An activation bar is a thin rectangle that is placed under a lifeline to represent the time it takes to complete a task. You can add multiple activation bars on the lifelines.
5. Include any other important features
In complex sequence diagrams, you can add Alternatives, Options, and Loops to represent different sequences.
Examples of a UML sequence diagram
Let's use the example of a fast-food restaurant's ordering system to understand how a sequence diagram works.
The following interactions take place during this sequence when a customer wants to place an order:
They go to the cash counter and place an order
The cashier confirms the order and gives order details to the kitchen
The kitchen staff prepare the food and deliver it back to the counter
The cashier hands the order to the customer.
A sequence diagram example for this scenario will have the customer, the cashier, and the kitchen as the three lifelines. They deliver messages back and forth.
The actions that take place during this sequence are the messages. Such as "Place an order," "Order confirmation," "Order details for preparation," and "Order delivery."
Benefits of using the UML sequence diagram template
Let’s walk through the four benefits of using a sequence diagram template.
1. Discover interface and logical problems early
Since creating a sequence diagram requires teams to flesh out all the details of a system, it helps them find problems well before the implementation phase.
2. Collaborate with teammates
A sequence diagram is an excellent option when you want to clearly depict how a system works or should work during team meetings or projects. Because of this, you can use it as a collaboration diagram.
3. Get a bird’s-eye view
With a sequence diagram, analysts can examine a system, whether that's a shopping kiosk or a new app, at various levels of abstraction. You can start with a high-level view of the system and then delve into the details as required.
4. Update it easily
Teams can update every element within a sequence diagram to match changing events or circumstances without overhauling the entire diagram.
What are the basic elements of a sequence diagram?
The most crucial elements of a sequence diagram are lifelines, messages, actors, and activations. There are more complex elements that can help depict complicated or recurring systems.
What does a sequence diagram show?
A sequence diagram shows how two or more elements within a system interact in the sequential order of their interaction. It is a UML diagram that highlights the sequence of messages passed between objects within an application.
What is the format of a sequence diagram?
A sequence diagram is a visual representation of how different components or objects interact with each other over time in a system. It typically includes vertical lifelines representing participants, horizontal arrows showing messages exchanged between them, and activation boxes indicating the time period for each participant's activity. The order of messages reflects the chronological sequence of interactions, and activation arrows show the focus of control during each step. Additional elements like loops, conditions, and parallel interactions can be represented using combined fragments. Although the format may vary depending on the modeling language or tool, these fundamental elements provide a clear understanding of the dynamic behavior within a system.
Get started with this template right now. Available on Enterprise, Business, Education plans.
5-Set Venn Diagram
Works best for:
Venn Diagram
Analyze complex data with the 5 Set Venn Diagram template. This tool allows you to compare and contrast five different sets of data, highlighting intersections and unique elements. Perfect for in-depth data analysis, research, and strategic planning. Ideal for analysts, researchers, and educators looking to present comprehensive data insights in a clear and visual manner.
SMART Goals Template
Works best for:
Prioritization, Strategic Planning, Project Management
Setting goals can be encouraging, but can also be overwhelming. It can be hard to conceptualize every step you need to take to achieve a goal, which makes it easy to set goals that are too broad or too much of a stretch. SMART is a framework that allows you to establish goals in a way that sets you up for success. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely. If you keep these attributes in mind whenever you set goals, then you’ll ensure your objectives are clear and reachable. Your team can use the SMART model anytime you want to set goals. You can also use SMART whenever you want to reevaluate and refine those goals.
UML Class Diagram Template
Works best for:
UML Class Diagram Template, Mapping, Diagrams
Get a template for quickly building UML class diagrams in a collaborative environment. Use the UML class diagram template to design and refine conceptual systems, then let the same diagram guide your engineers as they write the code.
Value Stream Mapping Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Strategic Planning, Mapping
A value stream map can help you refocus your business on steps that actually provide value to your customers, cutting out wasteful and inefficient processes. With this template, you and your process team can collaborate on a value stream map today.
Opportunity Solution Tree Template
Works best for:
Flowcharts, Product Management, Diagrams
Solving problems — successful companies and productive teams just know how to do it. They’re able to identify many possible solutions, then settle on the one that leads to the desired outcome. That’s the power an Opportunity Solution Tree gives you. Designed by Teresa Torres, a product discovery coach, this mind map breaks down your desired outcome into opportunities for the product to meet user needs, then gives your team an effective way to brainstorm potential solutions.
4-Circle Venn Diagram Template
Works best for:
Diagramming, Mapping, Brainstorming
The 4-Circle Venn Diagram Template has an easy, interactive, and dynamic way to visualize complex relationships between data sets. Empower your team's collaboration and communication with this powerful tool.