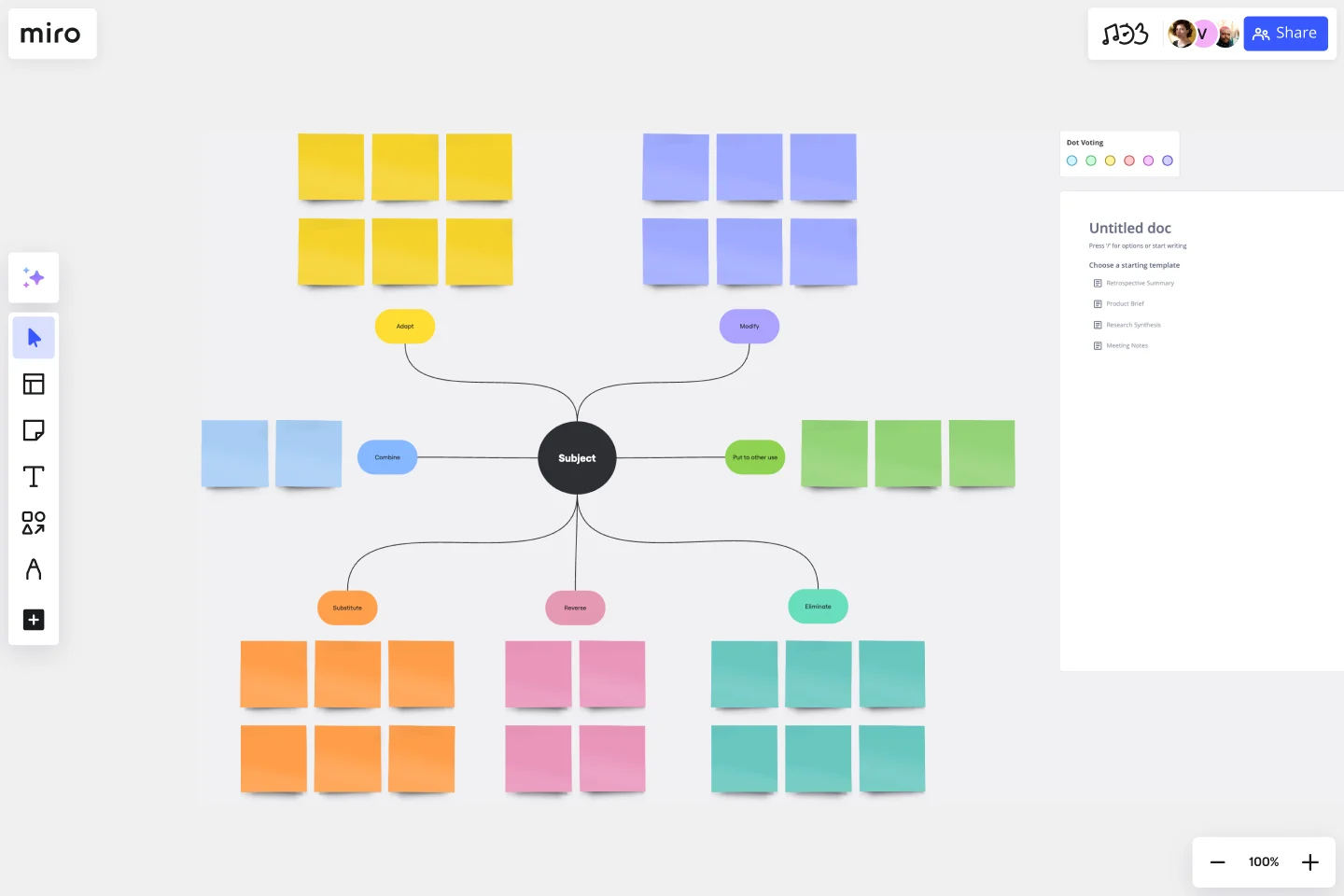
SCAMPER Model
View current and existing problems through the seven different SCAMPER lenses that help with brainstorming, creative thinking, and exploring new possibilities.
About the SCAMPER Model
What is a SCAMPER brainstorm?
SCAMPER is a brainstorming method developed by Bob Eberle, an author of creativity books for young people, who introduced it in his 1971 book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. In this clever method, you’ll find 7 different questions to encourage and inspire your team to approach a problem through 7 unique filters. By asking your team to think through a problem using this framework, you’ll unlock fresh, innovative ways to understand the problem you’re trying to solve.
What does the SCAMPER acronym stand for?
Substitute
Combine
Adapt
Modify (also Magnify and Minify)
Put to another use
Eliminate
Reverse
These keywords refer to 7 thought-provoking questions to ask during your brainstorm. The goal is to help you dig deep to find innovative solutions to problems your team or company faces. The 7 filters used for this exercise represent the questions necessary for busting through creative blocks to discover new ways to work.
When to use the SCAMPER model
Is your team in a rut? Have you had a lingering problem that can’t seem to be solved? Are you starting a new initiative at work? SCAMPER is a great way to get unstuck and move past stagnant, outdated ideas to new, more enlightened ones. Use this technique to help your team explore outside traditional ways of thinking through 7 different perspectives.
SCAMPER is considered one of the easiest, most direct brainstorming methods. The simple technique is based on the idea that what’s new is actually based on something that already exists. Any and all responses are welcome, no matter how random or illogical.
How do you use the SCAMPER method?
Starting a remote SCAMPER-based brainstorm is easy. Just open up your Miro Template and get started with the pre-populated layout. Pro Tip: the way to SCAMPER is nonlinear. If you’re moderating your team’s brainstorming, feel free to bounce fluidly between questions.
Step 1: Align your team to the problem you’re trying to solve.
This goes without saying for every brainstorm, but it’s important to set clear goals before you start scampering.
Step 2: Begin working through each letter in SCAMPER.
Here is a breakdown of the method, and some questions to help you get your team’s creative juices flowing.
Substitute: The questions to ask here are: What can you substitute or change—whether that’s your product, problem, or process? How can you substitute it for something else entirely?
Combine: When you get to this stage, you should consider how to combine two or more parts of your process or product in the hopes of achieving something new and different. For : perhaps two of your product features are getting in each other’s way. Can they be combined to create a more efficient customer experience?
Adapt: During the “adapt” phase of your brainstorm, think through what can be added, tweaked, or modified in your product or process to make it better. Sample questions include: How can we adjust the existing product? How can we make the process more flexible?
Modify: Could you modify the product, problem, or process to improve results? Can you change the process to work more efficiently?
Put to another use: Can the product or process be applied to a different use, or used in another way? What benefits would be gained by using the product elsewhere?
Eliminate: What can be removed or simplified? How can you achieve desired results without it? This step is all about purging aspects that do not bring anything to the table.
Reverse: Could your team rearrange or interchange elements to improve results? Is flipping your product or process on its head something your team should consider? Yes.
How is SCAMPER used in creative thinking?
The seven different SCAMPER questions are designed to inspire creative thinking by looking at a problem or solution through different lenses, which are not prescriptive. Any and all ideas are welcome to enhance this ideation exercise.
What are the advantages of SCAMPER?
The SCAMPER method encourages creativity in brainstorming by removing boundaries and also promotes constructive problem-solving among teams. For an optimal SCAMPER brainstorming session, it’s important to promote an environment that encourages new ideas where nobody feels that their contributions are dismissed.
What are examples of SCAMPER?
The SCAMPER method is designed to enhance creative thinking in problem-solving and examples of this can be seen across teams in the workplace and also with children in the classroom.
Get started with this template right now.
Timeline Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Flowcharts, Project Planning
A timeline displays a chronological order of important dates, and scheduled events. Timelines help product managers, project managers, and team members tell visual stories about progress and obstacles. Timelines enable teams to see at a glance what happened before, what progress is happening now, and what needs tackling in the future. Projects or products with specific purpose or deliverables should be based on a timeline to be successful. Use the timeline as a shared reference for start dates, end dates, and milestones.
Floor Plan Template
Works best for:
Operations, Workshops
Maybe you’re planning a big occasion or event. Or maybe you’re arranging seating structures and traffic flows that are more permanent. Either way, creating a floor plan—an overhead scaled diagram of the space—is equal parts functional and fun. This template will let you visualize how people will move about the space and know quickly if the space will do what you need, before you commit time, money, or resources. And you’ll be able to get as detailed as you want—finding the right measurements and dimensions, and adding or removing appliances and furniture.
RACI Matrix Template
Works best for:
Leadership, Decision Making, Org Charts
The RACI Matrix is an essential management tool that helps teams keep track of roles and responsibilities and can avoid confusion during projects. The acronym RACI stands for Responsible (the person who does the work to achieve the task and is responsible for getting the work done or decision made); Accountable (the person who is accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the task); Consulted (the people who provide information for the project and with whom there is two-way communication); Informed (the people who are kept informed of progress and with whom there is one-way communication).
Market Segmentation Matrix Template
Works best for:
Marketing, Strategic Planning, Product Management
Successful, compelling marketing begins and ends with knowing your audience — who they are, where they are, and what they want and expect. A market segmentation matrix will help you understand them on a deeper level. This business tool divides your target market into subsets based on demographics, geography, needs, interests, psychographics, or behavioral characteristics. You can then use these insights and data to hit it out of the park, by building better product, sales, and marketing strategies. Our template lets you set up and populate a Market Segmentation Matrix with ease.
Project Proposal Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Documentation, Project Planning
For any type of project, the Project Proposal template can be a crucial step toward clarifying the context, goals, and scope of a project to get stakeholder buy-in. A project proposal outlines what you want to accomplish, your goals, and how you plan to achieve them. Generally, a project proposal gives the reader some context on the project, explains why it is important, and lists the actions that you will take to complete it. Project proposals have myriad uses. Often, businesses use project proposals to get external buy-in from a donor or outside stakeholder. But many companies draw up project proposals for internal buy-in too.
Product Brief Brainstorm Template
Works best for:
Product , Product Management
The Intelligent Product Brief Brainstorm template in Miro is crafted to supercharge your product development process. One standout benefit of this template is its AI-powered capabilities that elevate your brainstorming sessions. Not only does it help in organizing and capturing ideas, but it also provides additional insights and solutions, ensuring a thorough and innovative approach to problem-solving. This intelligent feature significantly cuts down the time spent on synthesizing information, allowing teams to concentrate on refining and implementing the best ideas, ultimately leading to more effective and efficient product development.